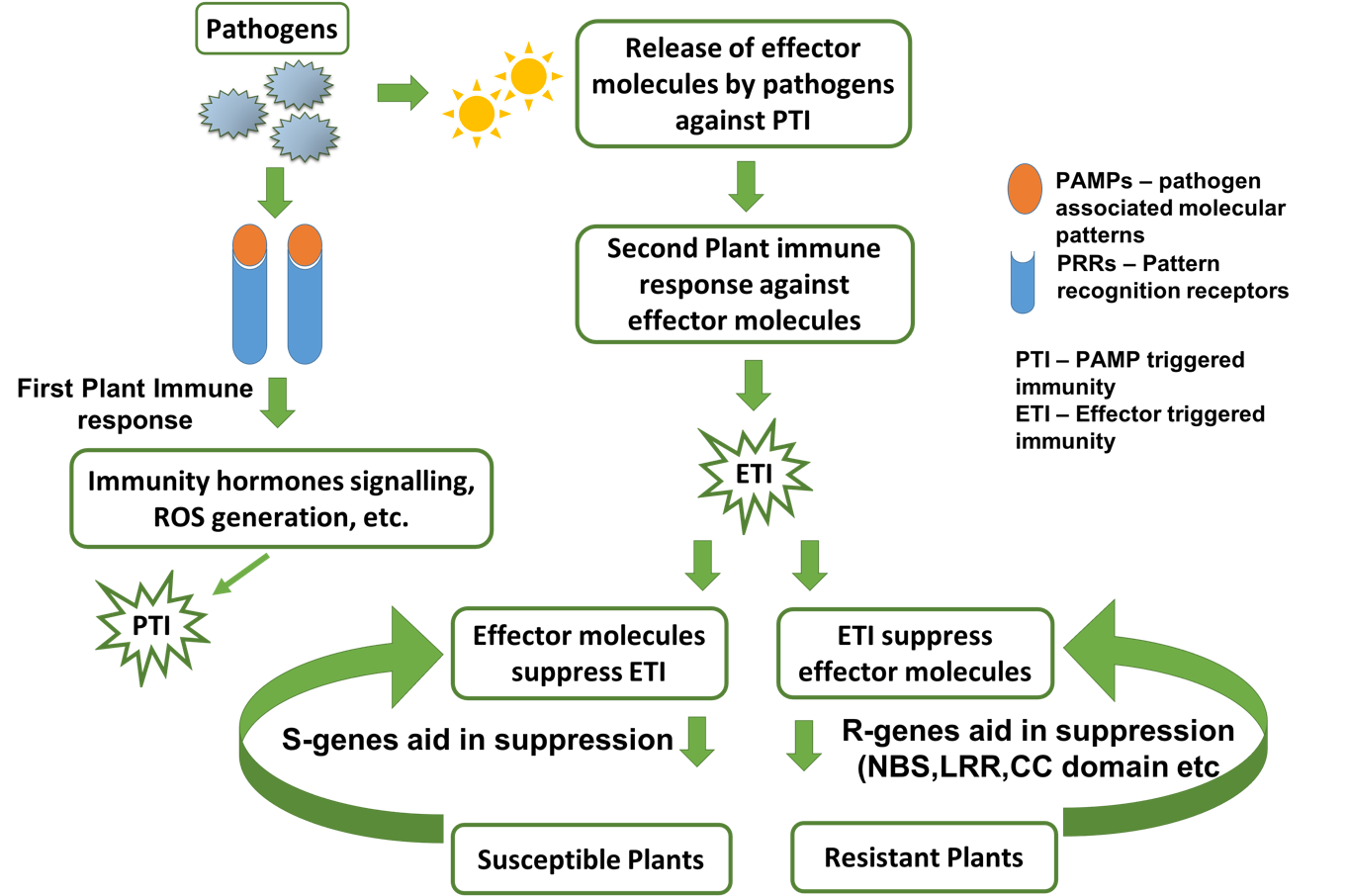
DSP: A database of Disease Susceptibility Genes in Plants
Plant pathogens such as viruses, bacteria, fungi, nematodes, and herbivores are the major biotic factors that are mainly responsible for low crop productivity during both pre-/post-harvesting times which ultimately affects global food security. From past several years resistance (-R) genes are exploited in wild species and cloned to cultivated varieties to break-up host-pathogen compatible interactions. However, co-evolution of pathogens with host break this compatible interactions and leads to disease in a few years. On the other hand, disease susceptible (S-) genes that are either negative regulators of immunity or encode proteins required for host plant development are manipulated by the plant pathogens for their growth and survival. Therefore, the identification and targeting of disease susceptible (S-) genes are gaining much more attention for the acquisition of disease resistance in plants. Further, genome engineering of S-genes results in targeted, transgene-free gene modification through CRISPR/Cas mediated technology and has been reported in several agriculturally important crops for improving plant health. Despite the great importance of S-gene in genome engineering for developing disease free crops, no database avaialble for public use.
In this work, we have compiled a literature curated database of S-genes known as "DSP (Disease Susceptible Gene in Plants)" from different crops that could be either used directly or searching for orthologs in new species for genome editing. DSP consist of ~500 genes from 24 crops including field, vegetable and horticultural crops. Also, five classes of pathogens including Bacteria, Fungi, Nematodes, Virues, and Oomycetes were described for disease condition in the database. In addition to that we have provided tools for SSR marker identification, primer designing and BLAST tool for orthologs identification. User can also downloads the data for gene, cds and protein sequences in fasta format for further usage.